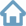
On September 18, 2022, the 1st stage of the 89th voyage of the RV Akademik Mstislav Keldysh to the Kara Sea with associated work in the southern part of the Barents Sea is completed in the port of Murmansk.
Expedition "Ecosystems of the Seas of the Siberian Arctic - 2022: Processes in the Arctic Continental Slope", carried out as part of a multi-year program of multidisciplinary research in the Kara Sea under the scientific supervision of Academician M.V. Flint, was divided into two stages. The 1st stage, lasting 14 days, took place from September 5 to 18 under the leadership of M. Kravchishina - the head of the expedition, A. Klyuvitkin and A. Novigatsky - the deputy heads of the expedition.
10 detachments and groups worked on the voyage, carrying out multidisciplinary research in almost all geospheres of the Earth (from the atmosphere to the lithosphere). The scientific team, united by a common task on board the vessel, included 60 specialists, graduate students and students from the IO RAS (Moscow, St. Petersburg, Kaliningrad, Arkhangelsk and Gelendzhik), the IOA SB RAS (Tomsk), GEOKHI RAS, FRC Biotechnology RAS, Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology , Lomonosov Moscow State University (Moscow), FRC MGI RAS and FRC InBYuM RAS (Sevastopol), St. Petersburg State University (St. Petersburg).
For the first time in the Kara Sea, synchronous studies were successfully carried out from the RV Akademik Mstislav Keldysh and from the Tu-134 Optik laboratory aircraft. The direct flight of the aircraft over the vessel at a distance of ~200 m from the sea surface took place twice on September 9 and 10, 2022. A unique climate experiment was carried out simultaneously in the Kara Sea and in Western Siberia, where lakes and research stations were selected for further comparisons of the land and sea contributions in air and aerosols.
Route and stations of voyage of AMK-89 1st stage
Research in the western part of the Kara Sea was primarily aimed at implementing work plans within the framework of the second year of the implementation of the project of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation to conduct large-scale world-class scientific projects using a unique scientific installation (USI) of the Tu-134 Optik laboratory aircraft. The work is carried out by a consortium consisting of 4 institutes of the Russian Academy of Sciences: the Zuev Institute of Atmospheric Optics SB RAS - the parent organization and executors - the Shirshov Institute of Oceanology RAS, the Obukhov Institute of Atmospheric Physics RAS and the Institute for Monitoring Climatic and Ecological Systems of the Siberian Branch RAN. Project Manager DrSc B.D. Belan (IOA SB RAS, Laboratory of Climatology of Atmospheric Composition), head of the contract on the part of IO RAS PhD V.P. Shevchenko.
The purpose of a large-scale scientific project is to study changes in the composition of air and characteristics of the underlying surface, including water, in the Russian sector of the Arctic and Siberia, in a changing climate by conducting synchronous ground, ship, aircraft measurements and numerical modeling to determine trends in their change for climate forecast and social - economic development of the region.
The main task of the voyage was the conjugate study of the conditions and processes of modern and ancient sedimentation in the western part of the Eurasian Arctic with an assessment of the fluxes of matter, greenhouse gases and pollution for the purposes of a reasonable forecast of the climate and environment of the future. Below we present only some of the current and expected results of multidisciplinary research during the expedition.
Signs of stable geological diffuse filtration of hydrocarbon gases (mainly methane) and solutions from the reservoirs of the South Kara oil and gas region have been reliably recorded. Dissolved thermogenic methane in sediments is associated with marine reservoirs of hydrocarbons formed as a result of thermal decomposition of organic matter (catagenesis). Microbial processes in bottom sediments (diagenesis), as a rule, mask the primary geochemical features of migrating gaseous fluids, significantly shifting the carbon isotopic composition of dissolved methane towards light values. The composition of hydrocarbons in sediments and particulate matter, as well as isotope-geochemical studies of hydrocarbon gases in the sedimentary stratum, carried out at the IO RAS and GEOKHI RAS (Laboratory of Carbon Geochemistry) will allow us to restore the nature of deep gas fluids.
The results of the study of ferromanganese nodules found on the bottom surface within the West Kara step will expand our understanding of the features of diagenesis processes in this area of the sea (IO RAS).
Based on the ecology of organisms found in fossil biocenoses, many physicochemical features of their habitat and burial in sediments will be restored, which will make it possible to confidently judge salinity, temperature, gas regime, water mobility in the geological past (IO RAS). In combination with isotope-geochemical and lithological data, the study of microremains of planktonic benthic organisms allows reliable reconstructions of paleoclimate to understand the mechanisms of climate change in the present and future.
Studies of hydrocarbons in the surface water microlayer, which is a geochemical barrier at the boundary of the atmosphere and hydrosphere, have been carried out. The concentration of hydrocarbons in the surface microlayer in suspended form has been established (IO RAS).
The collection of microplastic particles in the surface water layer of the Kara and Barents Seas was carried out. Potential plastic particles will be identified in a stationary laboratory using a Fourier transform IR spectrometer (IO RAS).
It is shown that the basis of the Yamal Current in Baydaratskaya Bay is melted coastal waters in the surface layer of the sea and the inflow of heavy and relatively cold waters of the East Novaya Zemlya Current in the near-bottom layer. Relatively warm Barents Sea waters penetrate into the northern part of the bay and approach the Yamal Peninsula.
Verification of signals from polarization lidar sounding of the surface layer of the sea with data on vertical distribution profiles of temperature, density, salinity, chlorophyll fluorescence and light attenuation index by water (IO RAS) was carried out, which will provide information on the position of the thermocline and suspension layers along the entire route of the vessel.
Under-aircraft measurements of the components of the energy balance of the subsurface layer of sea water were carried out using the UNU "Aircraft-laboratory Tu-134 "Optic"" at two test sites in the Kara Sea (IO RAS).
The film studio of the IO RAS filmed a short documentary film with the working title “Coccolito. Dancing over the Abyss”, which passed the competitive selection of the Regional Cinema Support Fund (Union of Russian Cinematographers “Russia – a look into the future”).
The expedition leadership expresses its deep gratitude to Academician M.V. Flint for support and invaluable assistance in organizing the expedition.
General photo of the expedition
The expedition was carried out with the financial support of the Russian Ministry of Education and Science (targeted funding for marine expedition research).